|
|
 |
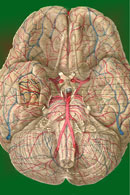
DIENCEPHALON
 |
Introduction
1) General Considerations:
•
The diencephalon
(through brain or betweenbrain) includes the thalamus,
hypothalamus, epithalamus, and subthalamus. It represents the
highest part of the brain stem and is capped by the
telencephalon (cerebral hemispheres). Except for the
interthalamic adhesion, the diencephalon is divided by the
cerebrospinal-fluid-filled third ventricle. It is bounded
caudally by the midbrain and rostrally by the frontal lobes of
the cerebrum.
|
 |
THE HYPOTHALAMUS
|
 |
THE THALAMUS
|
|
 |
 |
|
Prof. Munir Elias
Our brain is a mystery and to understand it, you
need to be a neurosurgeon, neuroanatomist and neurophysiologist.
neurosurgery.tv

Please visit this site, where daily neurosurgical activities are going
on.

Inomed ISIS IOM System
|
|
|
|