|
|
 |
THE BASAL NUCLEI
The white matter of the cerebrum is composed for the most part
of the myelinated axons of neurons with cell bodies located in
gray areas of the
CNS.
These gray areas include the cerebral cortex, thalamus, and
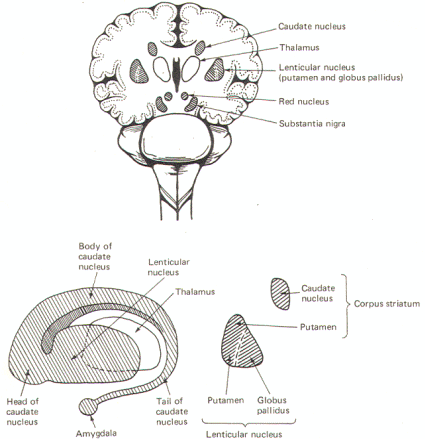
basal nuclei (Figs-1 and 2). The basal nuclei along with
the cerebellum play an important role in muscle coordination.
They include the caudate nucleus, putamen, globus pallidus, and
claustrum. However, the claustrum is often excluded when
describing the functional role of the basal nuclei in motor
control.
|
 |
 |
| Fig-1 |
Fig-2 |
The putamen is continuous anteriorly with the head of the
caudate nucleus, which arches upward and backward and
finally curves around anteriorly and laterally to enter the
temporal lobe ending in the amygdala (Fig-1). The caudate
nucleus and putamen are collectively called the corpus
striatum, while the putamen and globus pallidus represent
the lenticular nucleus. Taken together, the caudate
nucleus, putamen, and globus pallidus make up the basal
nuclei.
 |
The Internal
Capsule |
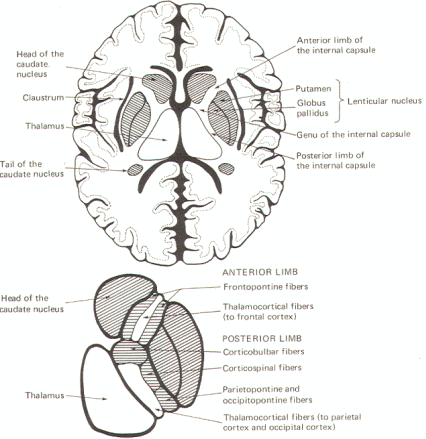
The oval thalamic mass lies just medial and posterior to the
lenticular nucleus on either side of the brain. With the
exception of the auditory radiation from the medial geniculate
body and the optic radiation from the lateral geniculate body,
all ascending and descending pathways between the cerebral
cortex and the brainstem pass through the internal capsule.
This vertical group of fibers is bounded laterally by the
lenticular nucleus, anteriomedially by the head of the caudate
nucleus, and posteriomedially by the thalamus (Fig-2). The corona radiata is a fanlike radiation of ascending and
descending fibers between the internal capsule and cerebral
cortex. In cross section, the internal capsule forms a V -shaped
region in each hemisphere (Fig-2). The principal ascending and descending fibers of the
internal capsule are also illustrated in this figure. The
anterior limb of the capsule is partly formed by the
frontopontine fibers which arise in the cortex of the frontal
lobe and descend to the pontine nuclei, where most of them
synapse. The anterior limb also carries ascending fibers of the
thalamocortical tract from the thalamus to the frontal cortex.
Corticobulbar fibers from the motor cortex to cranial nerve
nuclei controlling head and neck movements pass through the genu
and anterior part of the posterior limb. Also located in
the posterior limb, in increasingly posterior order, are
corticospinal fibers to the limb and trunk muscles and the
parietopontine and occipitopontine fibers connecting the
parietal and occipital cortex with pontine nuclei. Most of the
medial portion of the posterior limb is taken up by the
thalamocortical fibers, which project to the parietal and
occipital cortex.
|
 |
 |
|
Prof. Munir Elias
Our brain is a mystery and to understand it, you
need to be a neurosurgeon, neuroanatomist and neurophysiologist.
neurosurgery.tv

Please visit this site, where daily neurosurgical activities are going
on.

Inomed ISIS IOM System
|
|
|
|